Why Fast Websites Don’t Rank First? Practical Analysis 2026
It is the most common frustration in SEO today: You have optimized every image, minified every CSS file, and achieved a perfect 100/100 score on PageSpeed Insights. Yet, your competitors—whose sites feel slower and score lower—consistently outrank you on Google.
By 2026, the definition of "speed" has fundamentally shifted. Google no longer cares about how fast your site loads for a bot in a simulated environment. They care about how it feels to a real human user on a patchy 4G connection.
Key Takeaway: High PageSpeed scores are "Lab Data." Google ranks you based on "Field Data" (CrUX)—the actual experience of real users, which often tells a completely different story.
1. The "Lab Data" Illusion
Tools like Lighthouse run tests in a controlled environment. They don't account for:
- Network Variability: A user on a subway train vs. your fiber-optic office wifi.
- Device Fragmentation: Comparing a $1000 iPhone to a $150 budget Android phone.
- User Interaction: Lab tests barely scroll or click. Real users do.
2. TTFB: The Silent Killer
Time to First Byte (TTFB) is often ignored because many speed tools focus on "render" times. However, if your server takes 800ms just to start sending data, you have already lost the user's attention. fast rendering cannot save a slow server.
This is common in dynamic sites (WordPress, PHP apps) where database queries delay the initial response. Solution: Implement server-side caching (Redis, Memcached) or Edge Caching via a CDN.
3. Core Web Vitals in 2026: INP Over Everything
Since 2024, Interaction to Next Paint (INP) has replaced FID. It measures responsiveness. Does your menu open instantly when clicked, or is there a 300ms delay because the main thread is busy executing JavaScript?
Want to Improve Your Website Performance?
Get a free comprehensive analysis of your site speed and SEO performance in seconds
Check This: A site can load visually in 1 second (Good LCP) but be completely unresponsive for 3 seconds due to hydration or heavy analytics scripts. Google punishes this heavily.
4. Render-Blocking Resources
Modern sites often suffer from "CSS bloat." Loading a 500KB CSS framework for a page that uses 10KB of styles is a ranking signal suicide. Unused JavaScript is equally damaging.
- Action: Use code splitting. Only load the CSS/JS needed for the current viewport.
- Defer: Ensure non-critical scripts (chat widgets, tracking) are deferred until after LCP.
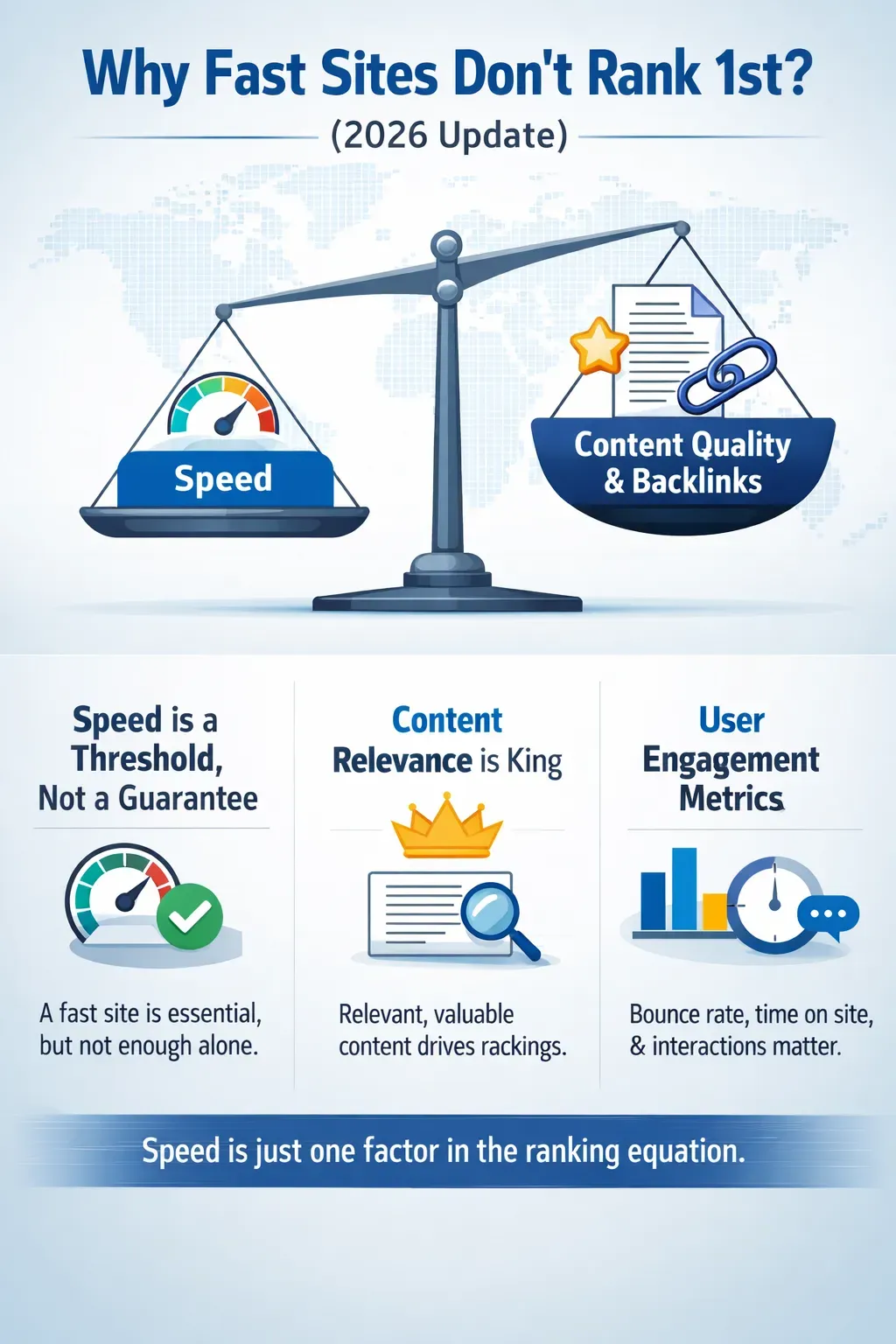
5. User Intent & Content Relevance
Finally, speed is a tie-breaker, not the primary ranking factor. A lightning-fast page with thin, irrelevant content will never outrank a "decently fast" page that perfectly answers the user's query.
The winning strategy for 2026: Combine elite infrastructure (Edge CDN, optimized database) with high-value, intent-matched content. Don't obsess over the 100/100 score; obsess over the Core Web Vitals "Pass" label in your Search Console.



No comments yet. Be the first to comment!