Preload is a powerful tool to enhance page load speed, but it can cause issues if not implemented correctly. This article highlights the most common technical mistakes in 2026 and shows practical ways to fix them.
1. Loading Unnecessary Resources
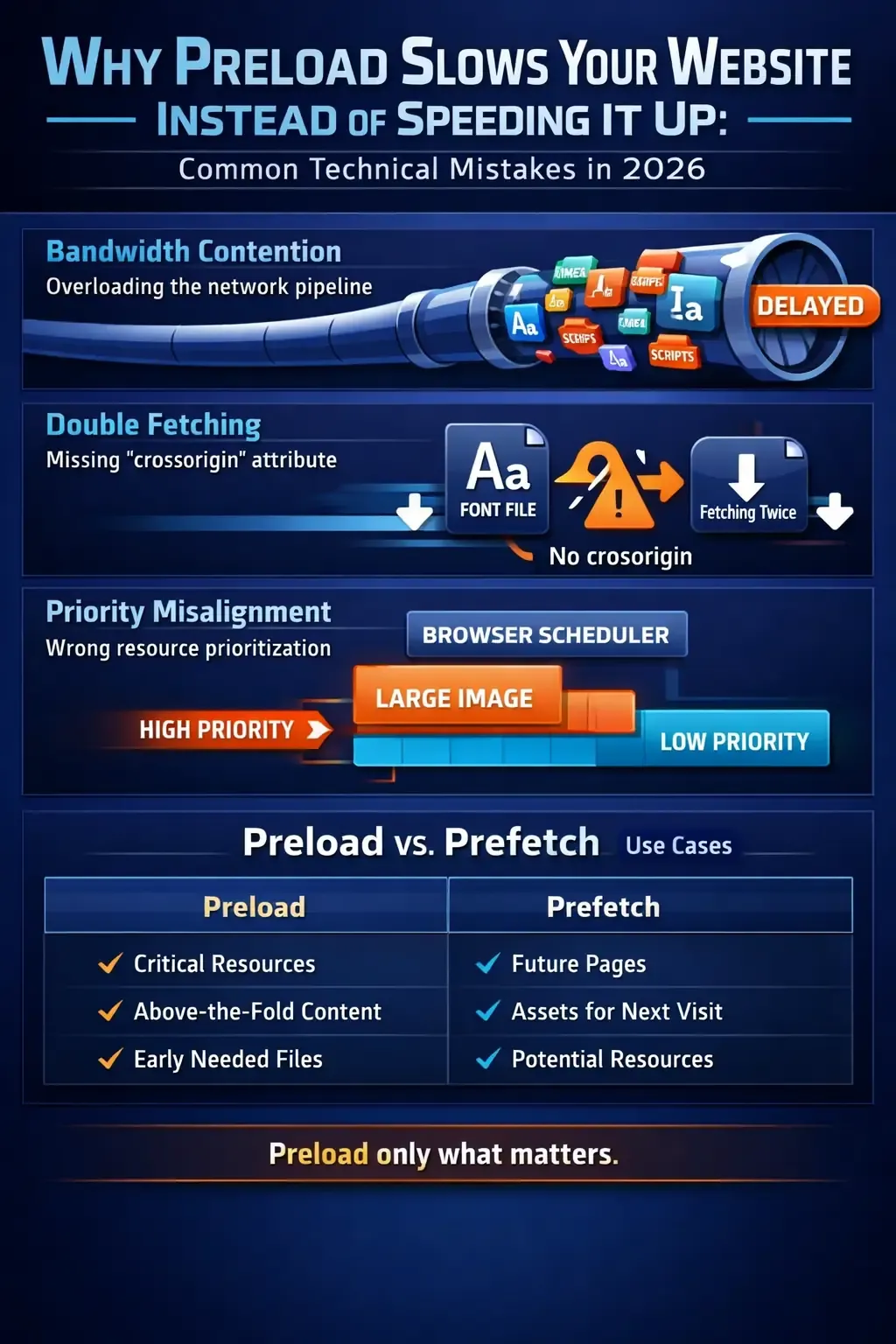
Many sites preload all fonts or scripts without prioritizing critical assets. The result:
- Wasted user bandwidth
- Increased initial load time
- Negative impact on Core Web Vitals
2. Incorrect Preload Order
Loading less important files before critical ones (like main CSS or primary fonts) leads to:
- Delayed rendering of main content
- Lower Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) score
3. Preloading Large Files
Example: Preloading a large image or heavy script can slow down your page instead of speeding it up. Fix:
- Compress images and JS files
- Lazy-load non-critical resources
4. Duplicating Preload for the Same Resource
Sometimes the same resource is preloaded multiple times, doubling requests and increasing load time. Fix:
- Review all <link rel="preload"> tags
- Ensure no duplicates exist
Want to Improve Your Website Performance?
Get a free comprehensive analysis of your site speed and SEO performance in seconds
5. Preloading Unsupported Resources
Some browsers ignore certain resources when preloaded (like some fonts or external scripts), causing:
- Unstable performance
- Poor user experience
Fix: Test Preload across all major browsers.
Practical Tips for Correct Preload Implementation
- Preload only critical resources
- Set Preload order by priority (CSS > Fonts > JS)
- Compress resources before preloading
- Test performance using free tools like PulsrWeb
- Avoid duplicates and unnecessary large files
Conclusion
Preload can significantly boost your website speed if used wisely. Common technical mistakes often cause delays instead of improvements. Following these practical steps ensures faster loading, better user experience, and improved SEO rankings in 2026.



No comments yet. Be the first to comment!